实验1 磁盘结构与文件系统
实验目的
加深对 FAT32 分区及文件系统格式的理解
掌握借助 WinHex 等工具手工定位磁盘文件数据的技能
通过开发一个磁盘文件数据提取工具,强化编程实践能力。
实验内容
内容一:手工定位和提取 FAT32 分区中的文件数据
在 FAT32 分区下创建一个不小于 10K 的文件,文件名称用本组组长姓名的拼
音命名。根据课上介绍的 FAT32 分区及文件系统知识,必要时自行上网查阅
相关资料,借助 WinHex 或其它十六进制工具,以手工方式从磁盘中逐一找
到该文件的各个存储扇区,复制其中的有效内容,并拼接组合成一个与原文
档内容相同的完整文档。
要求:操作过程描述中,要展示带有组长姓名字样的截图。
内容二:编程实现“内容一”的全过程
输入:某个文件(A)的路径
输出:
(1)该文件的短文件名目录项信息
(2)该文件的簇链
(3)根据上述的文件簇链,从磁盘上提取数据并拼接而得的新文件(B)
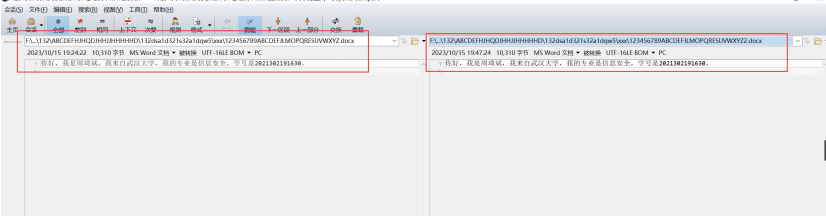
(4)文件 A 与文件 B 内容的比较结果(要求二者完全一致)
实验工具和编程语言
实验工具:Winhex、VSCode
编程语言:Python 3.9.12
实验步骤
内容一:
提前在新分区的 F 盘上创建 zqb.txt,并填入内容,文件大小 10K。
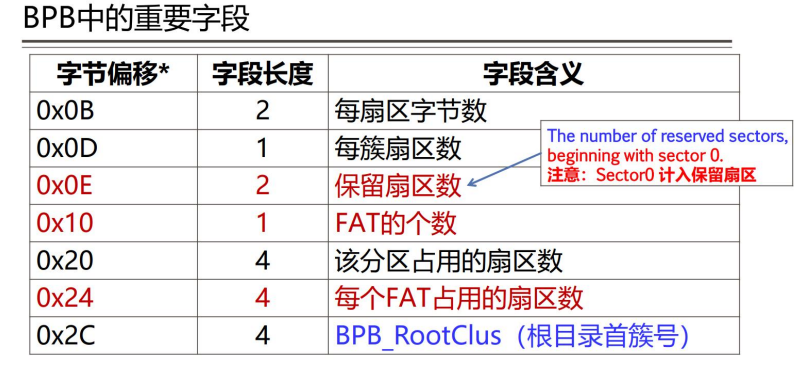
打开 Winhex,并且打开 F 磁盘。如下图,可得 BPB 中的重要字段:
·每扇区字节数:0x0200
·每簇扇区数:0x08
·保留扇区数:0x100E
·FAT 的个数:2
·每个 FAT 占用的扇区数:0x000007F9
·BPB_RootClus(根目录首簇号):0x02

故 FirstSectorofRoot=保留扇区数 + (FAT 个数 * 每个 FAT 所占扇区数)
=0x100E+(2*0x07F9)=0x2000
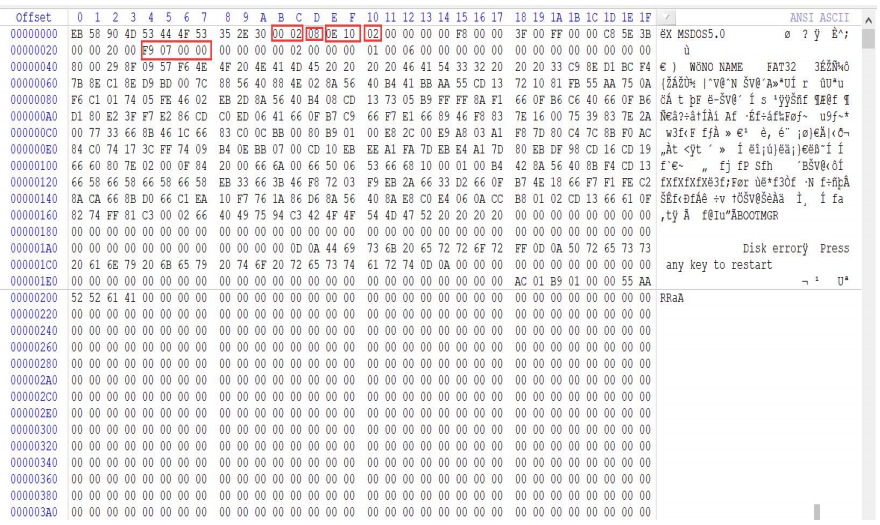
定位到 0x2000*0x200=0x400000 根目录处,找到 ZQB.TXT 在 0x4000E0 处。
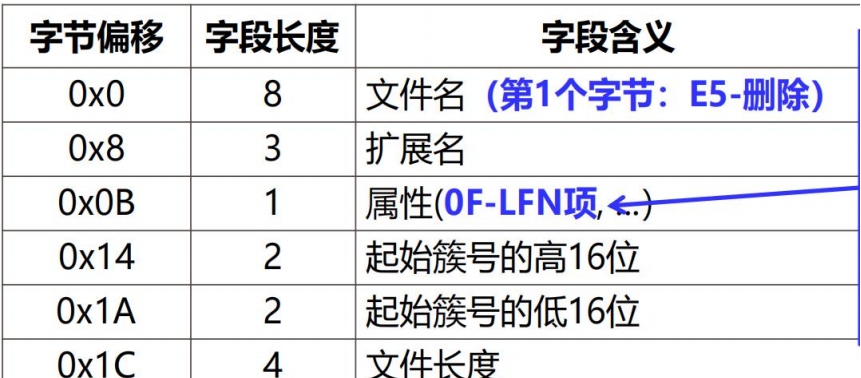
参考此表可得
·起始簇号的高 16 位=0x0001 ·起始簇号的低 16 位=0x022A
计算得起始簇号=0x0001022A
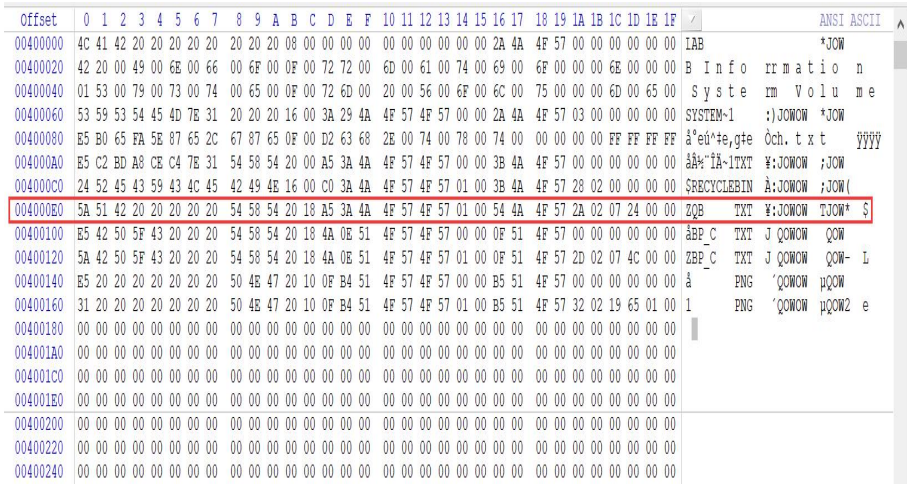
定位到 FAT1,即保留扇区数每扇区字节数=0x100E0x0200=0x201c00
起始簇号=0x0001022A,簇大小 4B,故位于 4*0x0001022A+0x201c00=0x2424A8
故起始簇的下一簇为 0x0001022B,下一簇=0x0001022C,再下一个为
0x0FFFFFFF,即最后一簇。

最后来定位文件,计算文件初始簇的偏移。根据下图的公式可得,
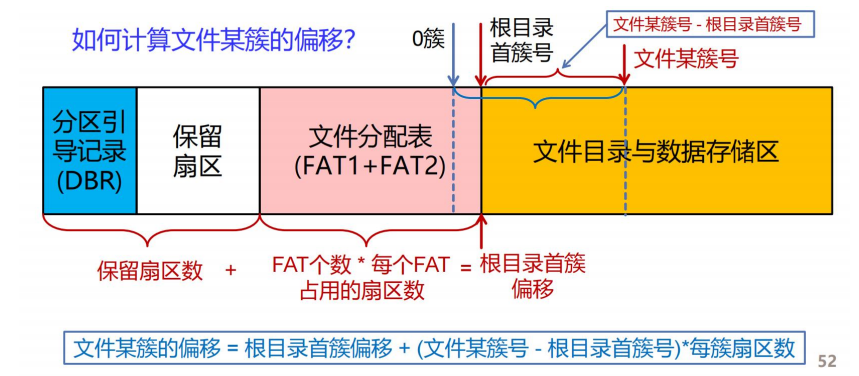
文件某簇的偏移 = 根目录首簇偏移 + (文件某簇号 - 根目录首簇号)*每簇
扇区数
zqb.txt 文件初始簇的偏移
=0x400000+(0x0001022A-0x2)80x200=0x10628000
可以发现,已经定位到 zqb.txt 文件。
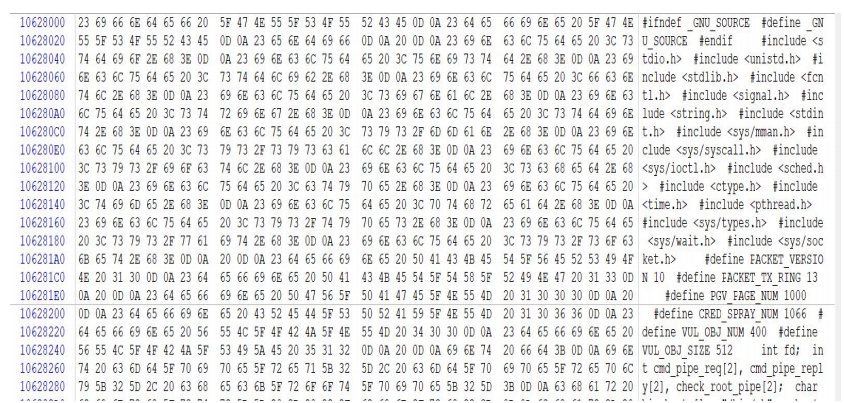
复制其中的有效内容拼接组合成一个与原文档内容相同的完整文档。

最后可成功打开
内容二:
程序主要设计思路
路径分割,打开磁盘
将输入的绝对路径进行分割,分割成一个一个的子文件(不区分文件和目录,
因为在磁盘中,目录其实就是特殊的文件)。
例如,对于输入的路径 F:/lab/123/test.txt,会将其分割成[“F:”, “lab”, “123”,“test” ]
读取磁盘
BPB 中的数据,主要数据如下
读取目录项
读取目录项时,要注意长文件名的单独处理,对于文件名大于 8 字节或者
文件后缀大于 3 字节的为长文件名。
首先由公式:FAT32 分区根目录项=保留扇区大小+文件分配表大小*文件分配
表个数 定位到根目录项。
然后通过根目录可以读取到一级目录的目录项,然后就可以通过一个循环去
读取二级、三级等目录项。
最后找到最后一级目录项,然后定位文件的首簇号,再定位其簇链(实验一
已经说明),最后就可以通过簇链定位文件内容。
读取文件内容并写入新文件
在第 3 步中,通过起始簇号可以在 FAT 中将文件的整个簇链找出来,然后就可以直接定位文件内容了。
读取文件内容时,要注意磁盘给文件分配存储空间时,是以簇为单位进行分配的。这也就是说文件的实际大小不一定就为操作系统给其分配的大小,所以这里在最后一簇时,要进行判断。
程序使用说明
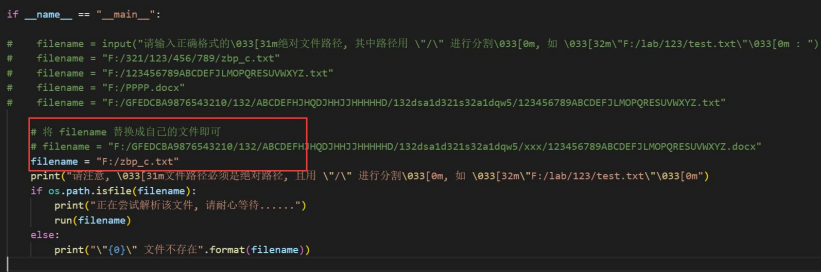
考虑到文件路径可能过长,所以只需要将文件路径替换成自己的路径即可,
注意文件路径应当是绝对路径,并且使用 “\” 进行分割,比如:F:/lab/123/test.txt
编程语句使用 python,所以无需编译,直接运行即可,如果出现语法错误,
可以是由于 python 版本导致,笔者使用的是 Python 3.9.12
程序测试结果
注意,如果文件目录过深,分析过程可能比较长,请耐心等待
测试 1:
输入文件内容及其路径:路径包含 6 级目录,并且包含长文件名及短文件名
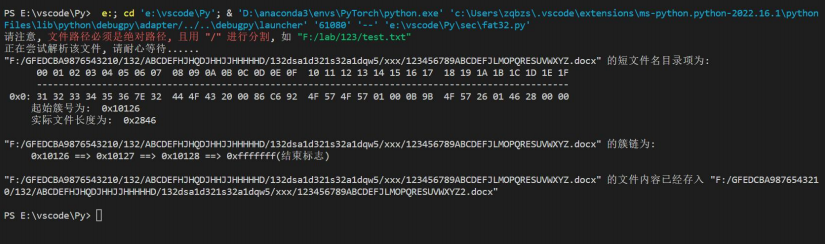
输出结果其新文件内容:
新旧文件对比:
测试 2:
输入文件内容及其路径:文件在根目录下,为短文件
输出结果:
新旧文件对比:
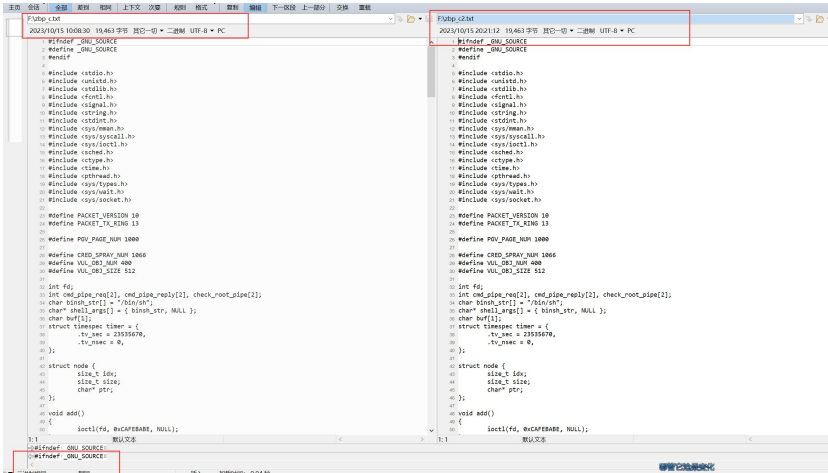
程序代码
import os
# 打印二进制数据, 方便 debug
def binary_dump(s, length=1000000000000000):
print(" "*(len(hex(len(s)))+2), end="")
for i in range(32):
if i % 8 == 0 and i != 0: print(" ", end="")
print(str.upper(hex(i)[2:].zfill(2)), end=" ")
print("\n "+"-"*98)
print(hex(0).rjust(len(hex(len(s))), " "), end=": ")
for i in range(len(s)):
if i >= length: break
if i % 8 == 0 and i != 0: print(" ", end="")
if i % 32 == 0 and i != 0:
print("")
print(hex(i).rjust(len(hex(len(s))), " "), end=": ")
print(str.upper(hex(ord(s[i]))[2:].zfill(2)), end=" ")
print("")
# 字符串转换为 16 进制数据
def str_to_hex(s):
return [hex(ord(i)) for i in s]
# 将 16 进制按照指定大小端进行转换
def hex_to_num(s, endian="little"):
hex_num, num = [int(i, 16) for i in s], 0
if endian == "big":
hex_num = [i for i in reversed(hex_num)]
# print(hex_num)
for i in range(len(hex_num)):
num |= hex_num[i] << (i*8)
return num
# 读取基本数据
def read_BPB(disk):
DBR = disk.read(512).decode(encoding='latin-1')
disk.seek(0)
# print(DBR)
# binary_dump(DBR)
DBR_hex = str_to_hex(DBR)
byte_per_sector = hex_to_num(DBR_hex[0xb:0xb+2])
sector_per_clust = hex_to_num(DBR_hex[0xd:0xd+1])
saved_sector = hex_to_num(DBR_hex[0xe:0xe+2])
fat_nums = hex_to_num(DBR_hex[0x10:0x10+1])
sector_per_fat = hex_to_num(DBR_hex[0x24:0x24+4])
root_clust_idx = hex_to_num(DBR_hex[0x2c:0x2c+4])
"""
print("byte_per_sector: ", hex(byte_per_sector))
print("sector_per_clust: ", hex(sector_per_clust))
print("saved_sector: ", hex(saved_sector))
print("fat_nums: ", hex(fat_nums))
print("sector_per_fat: ", hex(sector_per_fat))
print("root_clust_idx: ", hex(root_clust_idx))
"""
return byte_per_sector, sector_per_clust, saved_sector, fat_nums, sector_per_fat, root_clust_idx
# 寻找目录项
def find_file_dir_entry(filename, root_dir_entry_offset, disk, suffix="", max_len = 0x10000000):
k = 0
# 短文件名
if len(filename) <= 8 and len(suffix) <= 3:
while True:
dentry = disk.read(root_dir_entry_offset+0x20*k)
disk.seek(0)
# print(dentry[-0x20:])
dentry = dentry.decode(encoding='latin-1')[-0x20:]
k += 1
# binary_dump(dentry)
# print("======================================")
# print(str(dentry[:len(filename)]))
# print(str(dentry[8:8+len(suffix)]))
# print(dentry[0])
if str(dentry[:len(filename)]) == str.upper(filename):
#print("good")
if len(suffix) == 0 or str(dentry[8:8+len(suffix)]) == str.upper(suffix):
# print("good")
break
if k > max_len:
return [], False
return dentry, True
# 长文件名
else:
continue_flag = False
idx = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 28, 30]
length = len(filename)+len(suffix)
dentry_num = length // 13 + 1
first_num = length % 13
if len(suffix) != 0: file_name = filename+"."+suffix
else: file_name = filename
file_name_list = []
for i in range(dentry_num-1):
file_name_list.append(file_name[i*13:i*13+13])
if first_num: file_name_list.append(file_name[(dentry_num-1)*13:])
file_name_list = [i for i in reversed(file_name_list)]
#print(file_name_list)
#print(first_num)
while True:
if k > max_len:
return [], False
continue_flag = False
dentrys_origin = disk.read(root_dir_entry_offset+0x20*(k+dentry_num+1))
disk.seek(0)
dentrys_origin = dentrys_origin.decode(encoding='latin-1')[-0x20*(dentry_num+1):]
#binary_dump(dentrys_origin)
dentrys = [dentrys_origin[i*0x20:i*0x20+0x20] for i in range(dentry_num+1)]
for i in range(len(dentrys)): dentrys[i] = str_to_hex(dentrys[i])
#print(dentry_num)
if int(dentrys[0][0], 16) == 0xe5:
k += 1
continue
if first_num:
for i in range(first_num):
#print(str.upper(file_name_list[0][i]))
#print(str.upper(chr(int(dentrys[0][idx[i]], 16))))
if str.upper(chr(int(dentrys[0][idx[i]], 16))) != str.upper(file_name_list[0][i]):
continue_flag = True
break
#else:
#print(str.upper(chr(int(dentrys[0][idx[i]], 16))), end="")
#print("good")
if first_num: m = 1
else: m = 0
for i in range(m, dentry_num):
for j in range(13):
if str.upper(chr(int(dentrys[i][idx[j]], 16))) != str.upper(file_name_list[i][j]):
continue_flag = True
break
#else:
#print(str.upper(chr(int(dentrys[i][idx[j]], 16))), end="")
if continue_flag == True:
k += 1
continue
else:
# binary_dump(dentrys_origin)
# print("good")
break
# print(dentrys)
# print(file_name)
# print(dentrys_origin)
# print(dentrys_origin[dentry_num*0x20:])
return dentrys_origin[dentry_num*0x20:], True
# 通过目录项获取起始簇号
def get_clust_idx_and_file_size_by_dentry(dentry):
dentry_hex = str_to_hex(dentry)
# print(dentry_hex)
high = dentry_hex[0x14:0x14+2]
low = dentry_hex[0x1a:0x1a+2]
clust_idx_hex = low + high
# print(high)
# print(low)
# print(clust_idx_hex)
clust_idx = hex_to_num(clust_idx_hex)
file_size = hex_to_num(dentry_hex[0x1c:0x1c+4])
# print(hex(clust_idx))
return clust_idx, file_size
# 通过起始簇号在 FAT 表中找出簇链
def get_clust_list_by_fat(clust_idx, fat_offset, fat_size, disk):
clust_idx_list, flag = [], True
fat = disk.read(fat_offset+fat_size)[fat_offset:].decode(encoding='latin-1')
disk.seek(0)
# binary_dump(fat, 0x100)
fat_hex = str_to_hex(fat)
while True:
# print(hex(clust_idx))
clust_idx_list.append(clust_idx)
clust_idx = hex_to_num(fat_hex[clust_idx*4:clust_idx*4+4])
if clust_idx == 0xffffff7:
print("出现坏簇{0}".format(hex(clust_idx)))
break
if clust_idx == 0xfffffff or clust_idx == 0xffffff8: break
if clust_idx >= 2 and clust_idx <= 0xfffffef:
continue
else:
break
return clust_idx_list
# 找目录项, 其实就是对 find_file_dir_entry 的一个封装, 这里我只是为了方便而已
def find_sub_dir_clust_idx_list(dir_name, parent_clust_idx_list, root_dir_entry_offset, root_clust_idx, sector_per_clust, byte_per_sector, disk, suffix=""):
flag, dentry = False, ""
for clust_idx in parent_clust_idx_list:
if flag: break
"""
file_clust_offset = root_dir_entry_offset + (clust_idx - root_clust_idx)*sector_per_clust*byte_per_sector
# print("file_clust_offset:", hex(file_clust_offset))
content = disk.read(file_clust_offset+sector_per_clust*byte_per_sector)[file_clust_offset:].decode(encoding='latin-1')
disk.seek(0)
for i in range(0, len(content), 0x20):
dentry = content[i:i+0x20]
if str(dentry[:len(dir_name)]) == str.upper(dir_name):
flag = True
break
"""
dir_offset = root_dir_entry_offset + (clust_idx - root_clust_idx)*sector_per_clust*byte_per_sector
max_len = sector_per_clust*byte_per_sector // 0x20
dentry, flag = find_file_dir_entry(dir_name, dir_offset, disk, suffix, max_len)
return dentry
# 读取文件内容并写入新文件
def read_file_by_clust_list(filename, suffix, clust_idx_list, file_size, root_clust_idx, root_dir_entry_offset, sector_per_clust, byte_per_sector, disk):
with open(filename+"2."+suffix, "wb") as f:
for i in range(len(clust_idx_list)):
clust_idx = clust_idx_list[i]
file_clust_offset = root_dir_entry_offset + (clust_idx - root_clust_idx)*sector_per_clust*byte_per_sector
content = disk.read(file_clust_offset+sector_per_clust*byte_per_sector)[file_clust_offset:]
disk.seek(0)
if i == len(clust_idx_list) - 1 and (file_size % (sector_per_clust*byte_per_sector)) != 0:
content = content[:file_size-sector_per_clust*byte_per_sector*(len(clust_idx_list)-1)]
f.write(content)
print("\n\"{0}\" 的文件内容已经存入 \"{1}\"\n".format(filename+"."+suffix, filename+"2."+suffix))
def run(filename):
file_list_str = str(filename).split("/")
file_list_str[-1], suffix = file_list_str[-1].rsplit(".", maxsplit=1)[0], file_list_str[-1].rsplit(".", maxsplit=1)[1]
# print(file_list_str)
# print(suffix)
disk = open(r'\\.\\' + file_list_str[0], 'rb')
byte_per_sector, sector_per_clust, saved_sector, fat_nums, sector_per_fat, root_clust_idx = read_BPB(disk)
root_dir_entry_offset = (saved_sector + fat_nums*sector_per_fat) * byte_per_sector
# print(file_list_str)
# print("root_dir_entry_offset: ", hex(root_dir_entry_offset))
if len(file_list_str) == 2:
dentry, _ = find_file_dir_entry(file_list_str[1], root_dir_entry_offset, disk, suffix)
else:
dentry, _ = find_file_dir_entry(file_list_str[1], root_dir_entry_offset, disk)
# binary_dump(dentry)
clust_idx, file_size = get_clust_idx_and_file_size_by_dentry(dentry)
# print("clust_idx: ", hex(clust_idx))
# print("file_size: ", hex(file_size))
fat_offset = saved_sector * byte_per_sector
fat_size = fat_nums * sector_per_fat * byte_per_sector
# print("fat_offset: ", hex(fat_offset))
clust_idx_list = get_clust_list_by_fat(clust_idx, fat_offset, fat_size, disk)
for i in range(2, len(file_list_str)):
if i == len(file_list_str)-1:
dentry = find_sub_dir_clust_idx_list(file_list_str[i], clust_idx_list, root_dir_entry_offset, root_clust_idx, sector_per_clust, byte_per_sector, disk, suffix)
else:
dentry = find_sub_dir_clust_idx_list(file_list_str[i], clust_idx_list, root_dir_entry_offset, root_clust_idx, sector_per_clust, byte_per_sector, disk)
#binary_dump(dentry)
clust_idx, file_size = get_clust_idx_and_file_size_by_dentry(dentry)
#print("{0} 2".format(hex(clust_idx)))
clust_idx_list = get_clust_list_by_fat(clust_idx, fat_offset, fat_size, disk)
#print("{0} 3".format(i))
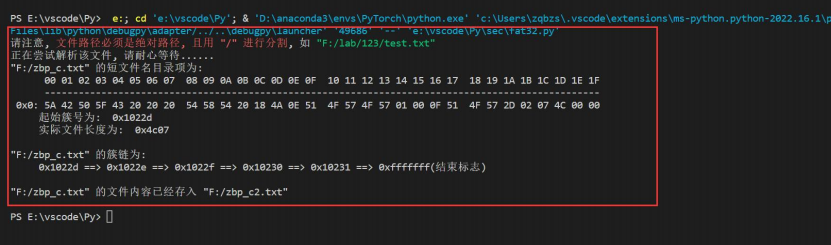
print("\"{0}\" 的短文件名目录项为: \n".format(filename), end="")
binary_dump(dentry)
print(" 起始簇号为: ", hex(clust_idx))
print(" 实际文件长度为: ", hex(file_size))
# 输出文件簇链
print("\n\"{0}\" 的簇链为: \n ".format(filename), end="")
for i in clust_idx_list:
print(hex(i), end=" ==> ")
print("0xfffffff(结束标志)")
read_file_by_clust_list(str(filename).rsplit(".", maxsplit=1)[0], suffix, clust_idx_list, file_size, root_clust_idx, root_dir_entry_offset, sector_per_clust, byte_per_sector, disk)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# filename = input("请输入正确格式的\033[31m绝对文件路径, 其中路径用 \"/\" 进行分割\033[0m, 如 \033[32m\"F:/lab/123/test.txt\"\033[0m : ")
# filename = "F:/321/123/456/789/zbp_c.txt"
# filename = "F:/123456789ABCDEFJLMOPQRESUVWXYZ.txt"
# filename = "F:/PPPP.docx"
# filename = "F:/GFEDCBA9876543210/132/ABCDEFHJHQDJHHJJHHHHHD/132dsa1d321s32a1dqw5/123456789ABCDEFJLMOPQRESUVWXYZ.txt"
# filename = "F:/GFEDCBA9876543210/132/xx.txt"
# 将 filename 替换成自己的文件即可
# filename = "F:/GFEDCBA9876543210/132/ABCDEFHJHQDJHHJJHHHHHD/132dsa1d321s32a1dqw5/xxx/123456789ABCDEFJLMOPQRESUVWXYZ.docx"
filename = "F:/zbp_c.txt"
print("请注意, \033[31m文件路径必须是绝对路径, 且用 \"/\" 进行分割\033[0m, 如 \033[32m\"F:/lab/123/test.txt\"\033[0m")
if os.path.isfile(filename):
print("正在尝试解析该文件, 请耐心等待......")
run(filename)
else:
print("\"{0}\" 文件不存在".format(filename))
声明
感谢组长大佬zqb的带领,没有他我肯定是不能独立完成实验全部内容。



